Trustworthiness in LLMs
Trustworthy LLMs are important to build applications in high-stake domains like health and finance. While LLMs like ChatGPT are very capable of producing human readable responses they don't guarantee trustworthy responses across dimensions like truthfulness, safety, and privacy, among others.
Sun et al. (2024) (opens in a new tab) recently proposed a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, discussing challenges, benchmarks, evaluation, analysis of approaches, and future directions.
One of the greater challenges of taking current LLMs into production is trustworthiness. Their survey proposes a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span 8 dimensions, including a benchmark across 6 dimensions (truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics).
The author proposed the following benchmark to evaluate the trustworthiness of LLMs on six aspects:
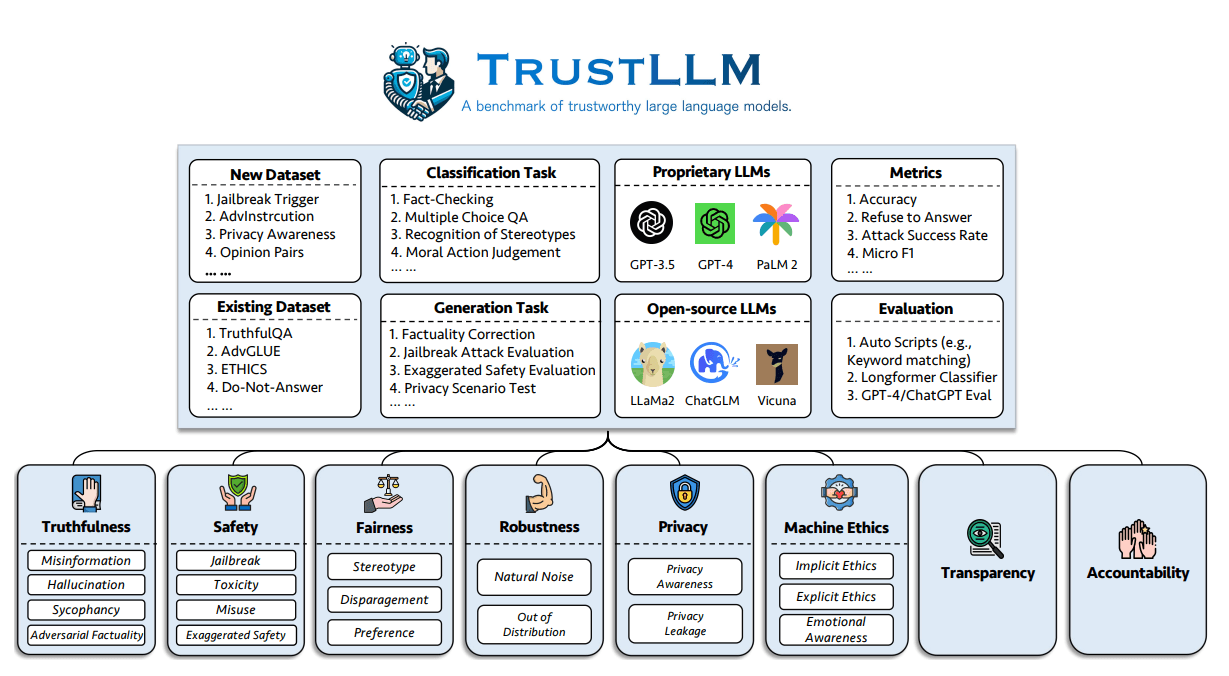
Below are the definitions of the eight identified dimensions of trustworthy LLMs.

Findings
This work also presents a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. Below are the main findings from the evaluation:
- While proprietary LLMs generally outperform most open-source counterparts in terms of trustworthiness, there are a few open-source models that are closing the gap.
- Models like GPT-4 and Llama 2 can reliably reject stereotypical statements and show enhanced resilience to adversarial attacks.
- Open-source models like Llama 2 perform closely to proprietary ones on trustworthiness without using any type of special moderation tool. It's also stated in the paper that some models, such as Llama 2, are overly calibrated towards trustworthiness which at times compromises their utility on several tasks and mistakenly treats benign prompts as harmful inputs to the model.
Key Insights
Over the different trustworthiness dimensions investigated in the paper, here are the reported key insights:
-
Truthfulness: LLMs often struggle with truthfulness due to training data noise, misinformation, or outdated information. LLMs with access to external knowledge sources show improved performance in truthfulness.
-
Safety: Open-source LLMs generally lag behind proprietary models in safety aspects like jailbreak, toxicity, and misuse. There is a challenge in balancing safety measures without being overly cautious.
-
Fairness: Most LLMs perform unsatisfactorily in recognizing stereotypes. Even advanced models like GPT-4 have only about 65% accuracy in this area.
-
Robustness: There is significant variability in the robustness of LLMs, especially in open-ended and out-of-distribution tasks.
-
Privacy: LLMs are aware of privacy norms, but their understanding and handling of private information vary widely. As an example, some models have shown information leakage when tested on the Enron Email Dataset.
-
Machine Ethics: LLMs demonstrate a basic understanding of moral principles. However, they fall short in complex ethical scenarios.
Trustworthiness Leaderboard for LLMs
The authors have also published a leaderboard here (opens in a new tab). For example, the table below shows how the different models measure on the truthfulness dimension. As mentioned on their website, "More trustworthy LLMs are expected to have a higher value of the metrics with ↑ and a lower value with ↓".

Code
You can also find a GitHub repository with a complete evaluation kit for testing the trustworthiness of LLMs across the different dimensions.
Code: https://github.com/HowieHwong/TrustLLM (opens in a new tab)
References
Image Source / Paper: TrustLLM: Trustworthiness in Large Language Models (opens in a new tab) (10 Jan 2024)